How to Mount Linux Remote Directories on Windows over SSH
Table of Contents
Vendor Description
WinFsp
WinFsp is a set of software components for Windows computers that allows the creation of user mode file systems. In this sense it is similar to FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace), which provides the same functionality on UNIX-like computers.
SSHFS-Win
SSHFS-Win is a minimal port of SSHFS to Windows. Under the hood it uses Cygwin for the POSIX environment and WinFsp for the FUSE functionality.
Installation and Setup of WinFsp and SSHFS-Win
- Download the latest release of WinFsp from their GitHub releases page. Just press on Assets under each release to get the
.msisetup file for example. - Install it on your Windows machine by simply double clicking the installer and following the setup.
- Download the latest release of SSHFS-Win from GitHub releases page. Again just press on Assets if you do not see the installer files.
- Install this on your Windows machine as well
Confirm that ssh is running on your server, e.g. with systemctl:
# systemctl status sshd.service
Mounting the Linux folder in Windows
Mounting in the GUI
If the sshd service is running, go to your Windows machine and press the Windows key and e key together to open the explorer. Right click anywhere and press Map network drive. In the Folder: input type \\sshfs\username@host where username is the name of the Linux user and the host is the hostname of the Linux machine or the IP-address. If the connect can be established, you will be asked for a password. This password is the password of the previously typed Linux user.
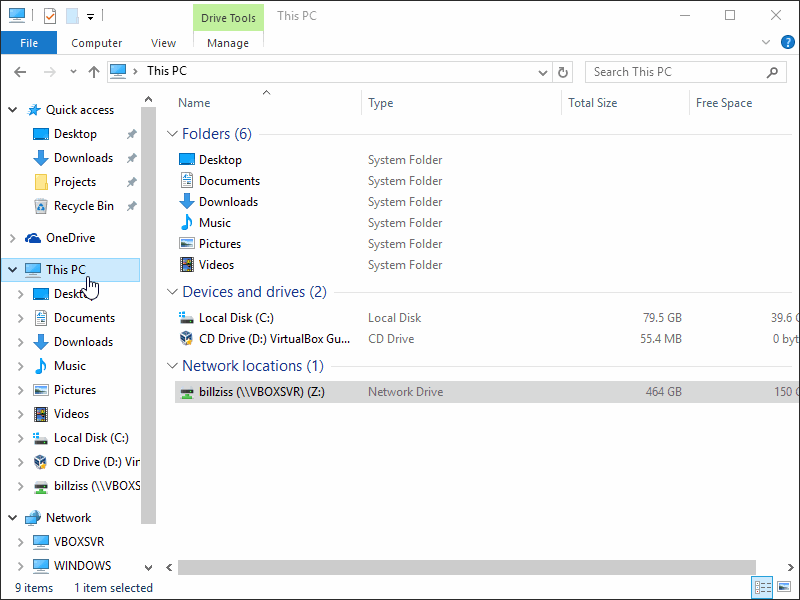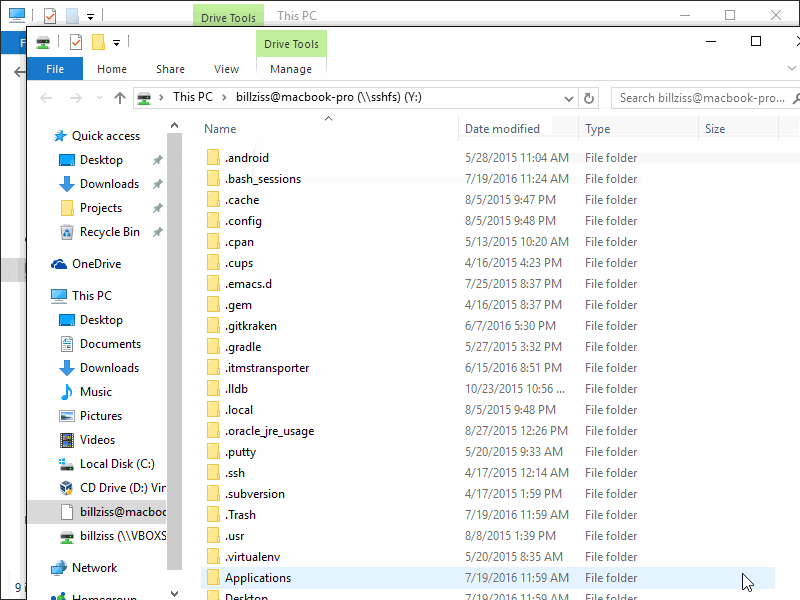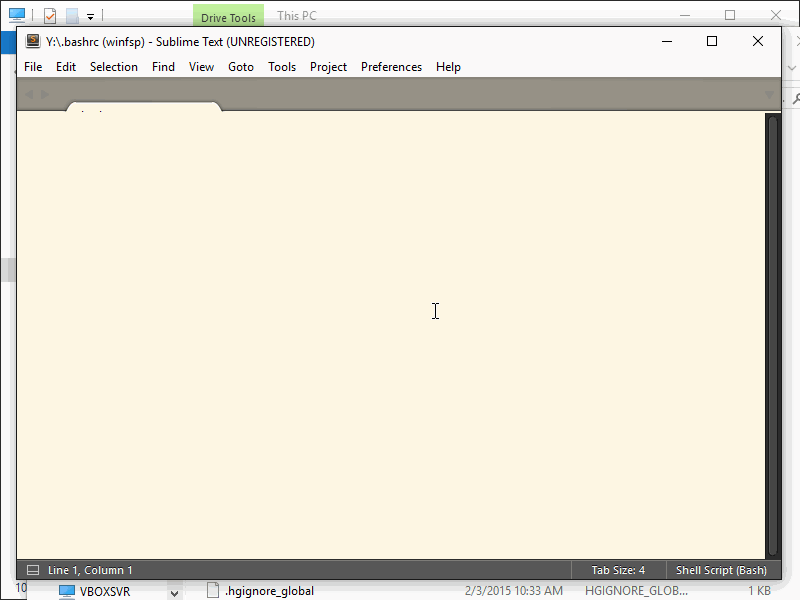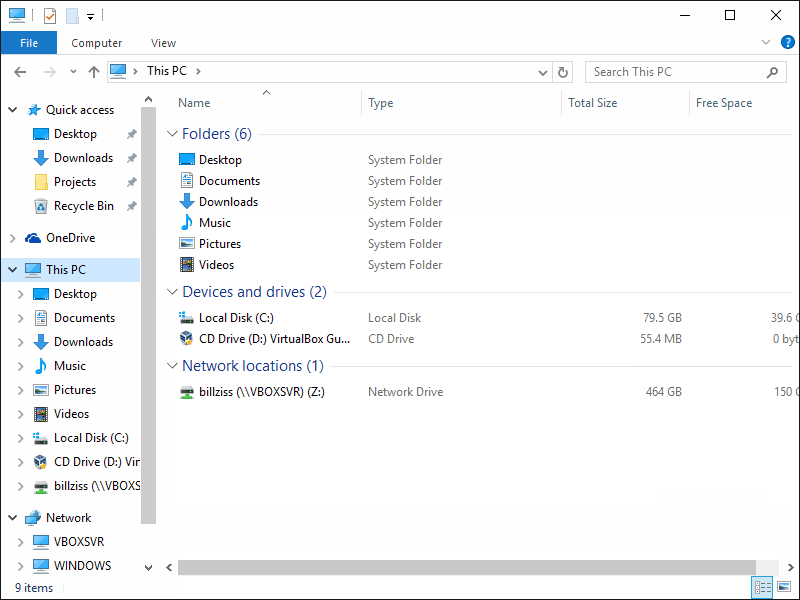 Demonstration on how to mount remote directory
Demonstration on how to mount remote directory
After this steps, the home folder of the user should be visible in the drive list of the explorer. Right click and disconnect to unmap the drive again.
There are also some GUI frontend available for SSHFS-Win:
Mounting via Commandline
You can also mount the folders using the commandline instead of the GUI the following way:
> net use X: \\sshfs\username@host
The password is invalid for \\sshfs\username@host.
Enter the user name for 'sshfs': username
Enter the password for sshfs:
The command completed successfully.
The unmounting process is in a similar fashion:
> net use Z: /delete
Z: was deleted successfully.
